[SpringBoot] Admin-project Main folder Guide
This is a sample script for SpringBoot practice. I recorded it to fully understand what I learned and did myself. It will remind me of SpringBoot development process.
Caution! This is my personal opinion so it’s unsystematic and definitely informal.
[Development environment]
MacOS / IntelliJ / MySQL
[Practicing…]
- SpringBoot version 2.1.7
- MySQL Workbench :: Database, ERD
- JPA :: Object-oriented
Development Process
It includes contents only about Main folder. Let’s go to see next post about Test folder!
👩🏻💻click here ➡ https://medium.com/@JynnPark/springboot-admin-project-test-guide-b067c782137f
0. Purpose
Project subject is Shopping Administration service. I practiced REST API. I basically operated CRUD through HTTP methods and JPA.
REST: Representational State Transfer
HTTP methods: POST, GET, PUT, DELETE
JPA: Java Persistence API
click here to get more information about REST API! https://gmlwjd9405.github.io/2018/09/21/rest-and-restful.html
00. Dependency
- Spring-Web-Starter
- Lombok
- Spring-Data-JPA
dependencies {
compile 'mysql:mysql-connector-java'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}1. Controller
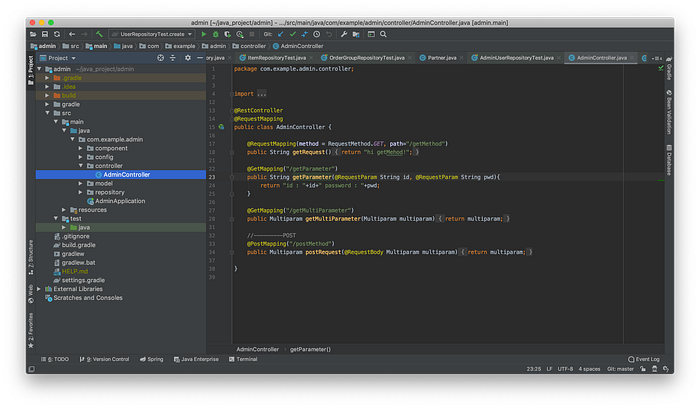
Controller handles URL from clients. I made a AdminController.java Class and embodied GET & POST for the first step. Especially I exported a Multiparam.java Class which responses to several parameters and I stored separately it at /Model folder.
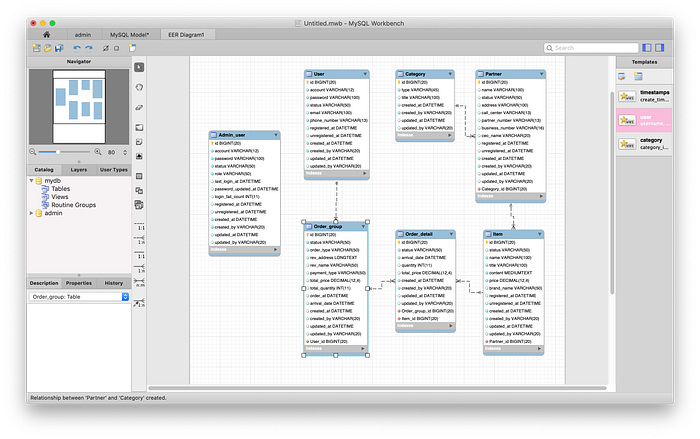
2. ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram)
I used MySQL Workbench tool. It’s on Database>Reverse Engineer menu. I selected ‘admin’ schema to export ERD. I indicated mutual association relationship among tables ‘One-to-Many’ or ‘Many-to-One’. It was applied on database automatically after Forward engineer.
3. Tables
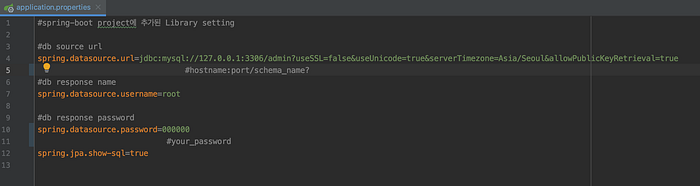
I put library setting at resources>application.properties to link MySQL database.
#db source url
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/schema_name?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=Asia/Seoul&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true
#db response name
spring.datasource.username=root
#db response password
spring.datasource.password=your_password
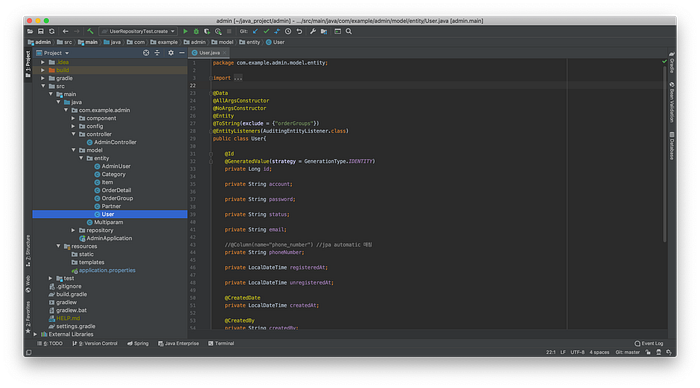
I made each Class in /entity folder following to database. SpringBoot automatically synchronizes “CamelCases” in Class and “snake_cases” in database. Then I put annotations @Entity on the Class and @Id, @GeneratedValue on prime key.
@Entity
public class Restaurant {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
...
}
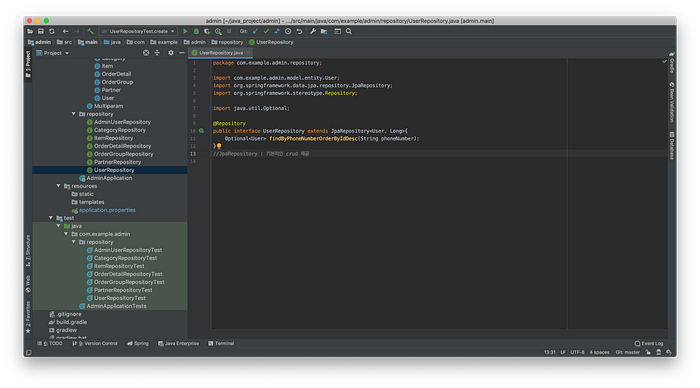
4. Repository
Next, I made each Interface Class in /Repository folder matching to entities I created before. I recognized fact that JPA supports DI and that’s why I didn’t consider about implementation Class.
DI : Dependency Injection
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long>{
...
}
In fact, I used to made an interface Class in a repository and a RepositoryImpl.java Class at the same time. However, JPA supports DI in Spring so I should delete all implementation Classes and add @Autowired directly to the object that I use in Test. instead.
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;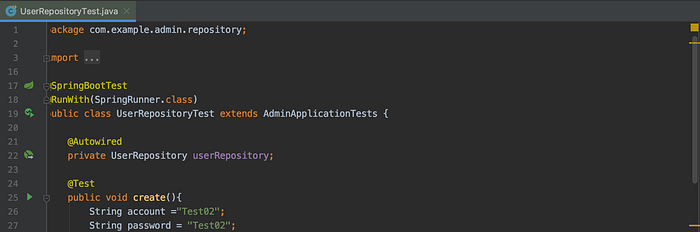
Take a look at a git commit history in another project. I had made RestaurantRepositoryImpl.java Class like underneath picture because interface Class needs a impl Class. However, I had to delete all impl Classes in next step to adopt JPA.
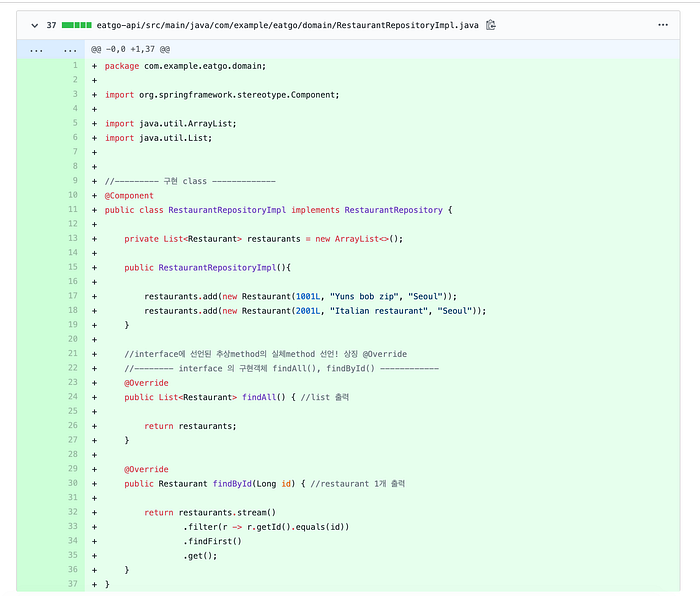
05. Set Association Relationship
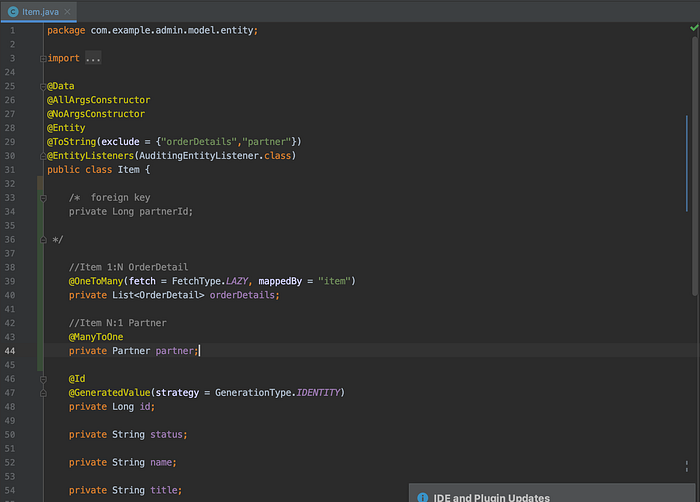
I set association relationship in ERD step in advance. According to those relationship, I removed foreign key which was in Entity Class and coded new fields with annotation. Especially I was care about the name which I put on mappedBy= “opponent_object_name” in @OneToMany to be same as object name in the opponent associated Class.
Also, I annotated @ToString(exclude={“ object_name ”}) on the Class and object_name was referred to object name in that Class.
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
@ToString(exclude = {"orderDetails","partner"})
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class Item {
.../* foreign key
private Long partnerId;
*/ //Item 1:N OrderDetail
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "item")
private List<OrderDetail> orderDetails;
//Item N:1 Partner
@ManyToOne
private Partner partner; ...
}

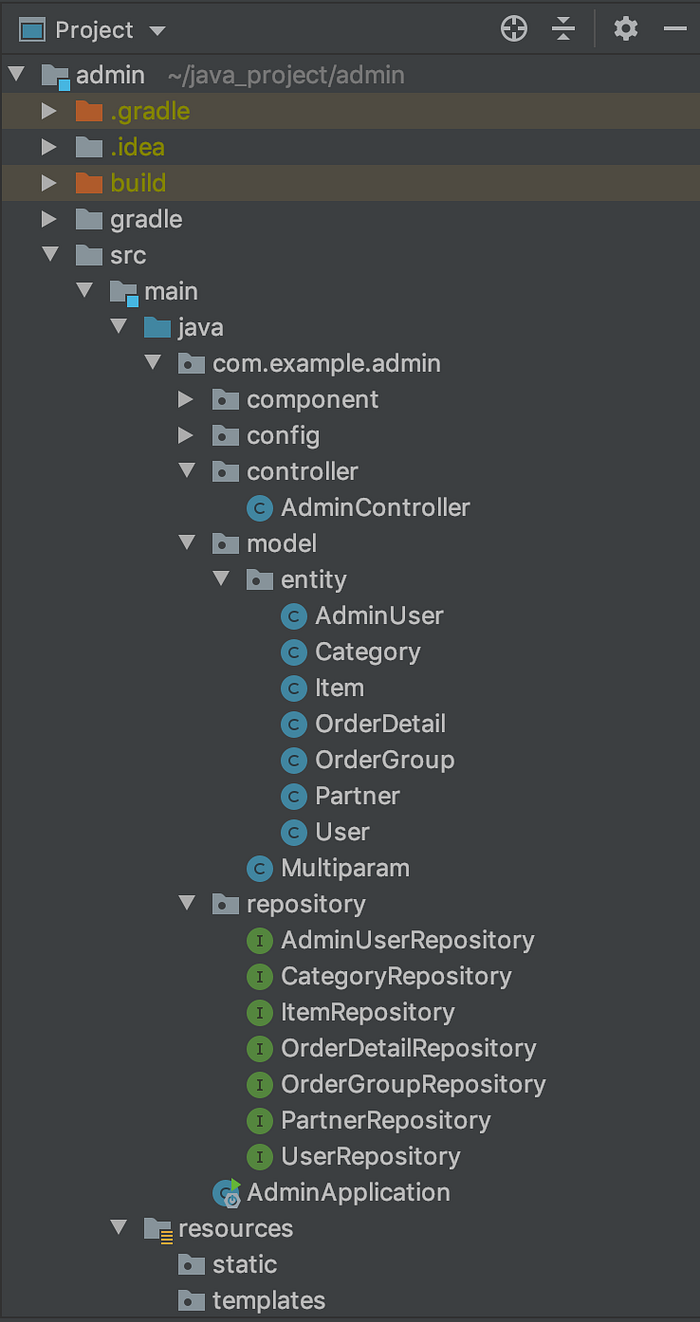
I finally set basic project structure in Main folder.
👩🏻💻click here to see next post about Test folder ➡ https://medium.com/@JynnPark/springboot-admin-project-test-guide-b067c782137f
👩🏻💻click here to see all project files ➡➡ https://github.com/jyuunnii/SpringBoot_project_admin.git